Trusted by over 5,000 Candidates
Updated: 14.9.2025
Also, see our free PDF guide.
What is the Elevator Industry Aptitude Test [EIAT]?
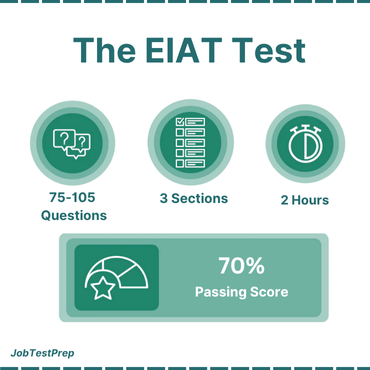
The Elevator Industry Aptitude Test (EIAT) is a 75-105 multiple-choice question exam designed to assess skills needed for elevator apprenticeships.
It's used by the National Elevator Industry Educational Program (NEIEP) for elevator apprenticeship applications.
Below, you’ll find free elevator practice questions in two formats: Timed and untimed, from our PrepPack. Try both to get a sense of the exam’s difficulty level.
Free Elevator Industry Aptitude Practice Questions
The elevator assessment includes 3 sections – Numerical Reasoning (Math), Mechanical Aptitude, and Verbal Reasoning. It is followed by an additional Tool Recognition test.
Let's start with some math sample questions.
Numerical Reasoning (Math) Sample Questions
To get a better sense of what our practice tests look like, take this free interactive assessment.

Under time pressure (see numerical question 1), convert decimals and fractions to whole numbers, solve, then add the decimal point back.
5732 x 0.001 = ?
A. 573.2
B. 57.32
C. 5.732
D. 0.5732
E. 0.05732
Answer:
A quick and simple trick to follow - the decimal point moves an equal amount of places on each side of the product in the opposite direction:
5732 x 0.001 =
= 573.2 x 0.01
= 57.32 x 0.1
= 5.732 x 1
= 5.732 - The answer is C.
0.55 - 2/10 = ?
A. 3/10
B. 7/20
C. 35/55
D. 53/100
E. 2/5
Answer:
0.55 - 2/10 = 55/100 - 20/100
= 35/100
Simplify by dividing 35/100 by 5
= 7/20 - The answer is B.
For more information, check out our free Numerical Reasoning Practice Guide.
Click the following page if you're looking for a comprehensive guide to kick-start your career and become an elevator mechanic.
Mechanical Aptitude Practice Questions
To get a better sense of what our practice tests look like, take this free interactive assessment.

When answering, rely on mechanical principles, not intuition. Pay attention to tricky wording, such as in mechanical question #1, where understanding the slope matters more than the distance.
Which cyclist has to pedal harder in order to go up the ramp?

A. a
B. b
C. The same
Answer:
In this question, we are asked which rider would need to pedal harder in order to climb the ramp.
We can see that though the ramps are of different lengths, the height of the logs in both cases is the same.
For this reason, we should understand that the shorter ramp will be steeper. As is known from daily life, it is harder to pedal up a steeper incline.
Since in Figure B, the length is shorter and the incline is greater, it would be harder to pedal up the ramp. Therefore, choice B is the correct answer.
Which tractor has to drive farther in order to bring the boat to shore?
A. 1
B. 2
C. The same

Answer:
Tractor 2 will drive in a straight horizontal heading, in the same direction as the boat is from the shore. This is the shortest line possible.
Tractor 1 will also drive in a horizontal line, but as it is tied to the boat diagonally it will therefore pull the boat over a larger distance.
However, tractor 1 will have to apply less force due to the mechanical help from the rock (the same as in a movable pulley).
For more mechanical questions, check out our EIAT Test Prep and practice your skills!
Verbal Reasoning Sample Questions
To get a better sense of what our practice tests look like, take this free interactive assessment.

When unsure about a sentence completion question, use the process of elimination. For example, in verbal question 1, eliminate A for grammar errors and C for illogical meaning. Begin by evaluating grammar, then logic.
Sentence Completion
"Since each person is ___________, collaborating as a team can bring __________ results."
A. talent … better
B. unique … superior
C. identical … inferior
D. different … continuous
Answer:
Since every person is unique (special), collaborating (working together) as a team can bring superior (better) results.
The first pair of words is not a good match because "talent" is a noun while the sentence calls for an adjective describing the person.
The third pair is incorrect because all people are not identical.
The fourth pair is incorrect because the adjective "continuous" does not make sense in the context of the sentence.
The last pair is incorrect because the word "diversity" is a noun and not an adjective.
Therefore, the correct answer is B - unique ... superior.
Grammar & Spelling
"Touch ID is ____ quite an elegant solution to an ever more ____ problem."
A. actually, singnificant
B. actully, signifikant
C. achtually, sigmificant
D. actually, significant
E. None of these
Answer:
The correct answer is D. Touch ID is actually quite an elegant solution to an ever more significant problem.
Incorrect Answers:
B and C can be eliminated because of the misspelling of 'actually'.
A has 'significant' misspelled.
For more information, check out our free EIAT Verbal Reasoning practice guide.
Follow a Proven Path to EIAT Confidence – Get Started Today
No more guessing. Our structured prep system walks you through:
Step 1: A diagnostic test that shows exactly what to focus on
Step 2: Smart practice by topic—mechanical, verbal, and numerical
Step 3: Full-length simulations (75 questions each) to lock in your skills under pressure
Bonus 🎁: Get 6 extra tools practice tests + NEIEP personality prep
Feel ready, not rushed— master the EIAT at your own pace.
See What People Say About Our Prep Pack
EIAT Tools Practice Questions
The EIAT has a separate tool assessment that's not part of the main EIAT score. This tool assessment will be given immediately after the aptitude test.
It contains questions about the names and uses of tools like diagonal cutters, tape measures, and lineman's pliers, as well as topics on meter reading.
Your performance on this tool assessment will influence your interview score.
Auto and Shop
A "Phillips" and a "flathead" refer to types of what tool?
A. Wrenches
B. Pliers
C. Screwdrivers
D. Hammers
Answer:
These are types of screwdriver heads. Phillips has a cross shape, while flathead is a straight line.

The correct answer is C.
Which of the items below is used for determining whether an item is horizontal?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 1
D. 5

Answer:
The object presented in image 1 is a level. A level is a device designed to indicate whether an object is horizontal or vertical. It consists of a vial filled with a liquid that leaves an air bubble;
the vial slightly curves upwards so that the bubble naturally rests in the middle, the highest point. When the device is slightly inclined, the bubble shifts to the side and away from the marked center.
The tool presented in image 4 is a square, which measures whether an object has a right angle but Isn't able to test whether it is leveled.
The tool presented in image 5 is a C-clamp, which is used for holding objects in place.
The object presented in image 2 is a wrench, which is used for tightening and loosening bolts.
The level is the only device that incorporates a gravity-dependent feature: the air bubble, which changes its position in the tube according to the highest point.
The correct answer is (C).
For more information, check out our free EIAT Tools Practice Guide.
Boost Your EIAT Confidence—Start Your Prep Now!
No more guessing. Our structured prep system ensures you're fully prepared with clear steps:
Step 1: Diagnose your strengths and focus areas.
Step 2: Practice smart—mechanical, verbal, and numerical topics.
Step 3: Simulate real test conditions (75 questions each).
Exclusive Bonus: 6 extra practice tests and NEIEP prep!
Feel ready, not rushed—master the EIAT at your own pace.
How to Pass the Elevator Industry Aptitude Test?
To pass the Elevator Industry Aptitude Test (EIAT) successfully, focus on strengthening your skills in mathematics, reading comprehension, and mechanical principles. Use practice tests and study guides to become familiar with the test format and question types.
Time management is key—practice solving problems quickly, especially in the numerical reasoning section, where calculators are not allowed. Also, watch the following video for more information.
How to Become an Elevator Installer?
To become an elevator installer, you generally must complete a four-year apprenticeship that blends classroom education with practical on-the-job training.
These apprenticeships are commonly offered through unions, industry groups, or individual contractors.
See the following guide for more information on how to become an elevator apprentice.
FAQs
How long is the EIAT test? The test lasts 90 minutes, with:
- Reading: 25 minutes
- Mechanical: 25 minutes
- Math: 40 minutes
If you fail, you won't move to the interview stage and will be removed from the applicant pool. You can re-apply in the next recruitment period.
A passing score is 70%. You must score at least this to continue. Applicants are ranked into four tiers, which are valid for two years
Results arrive after the test, along with your rank. A higher rank can help speed up your apprenticeship process.
Major companies, such as OTIS, Schindler, Thyssenkrupp, and WMATA, use the EIAT when hiring for the elevator industry.
If you pass with a 70% or higher, you'll be scheduled for an interview. Some may also need to take a tools test.
The interview lasts 15-20 minutes and covers education, experience, motivation, safety, and work behavior.